Our Technologies
Out-of-Autoclave processes for low-cost, rapid production of lightweight aerospace components
- Minimize weight of components and component systems
- Reduce production costs (cost savings on autoclave purchase and operation)
- Shorten cycle times
- Improve part performance (higher service temperatures, improved durability, increased stiffness)
Liquid Composite Molding
Applications:
- Best suited for medium to high rate production of complex, high performing structures
Benefits:
- Autoclave not necessary
- Materials less costly than pre-preg materials and can be stored at room temperature
- Cosmetic finish can be achieved
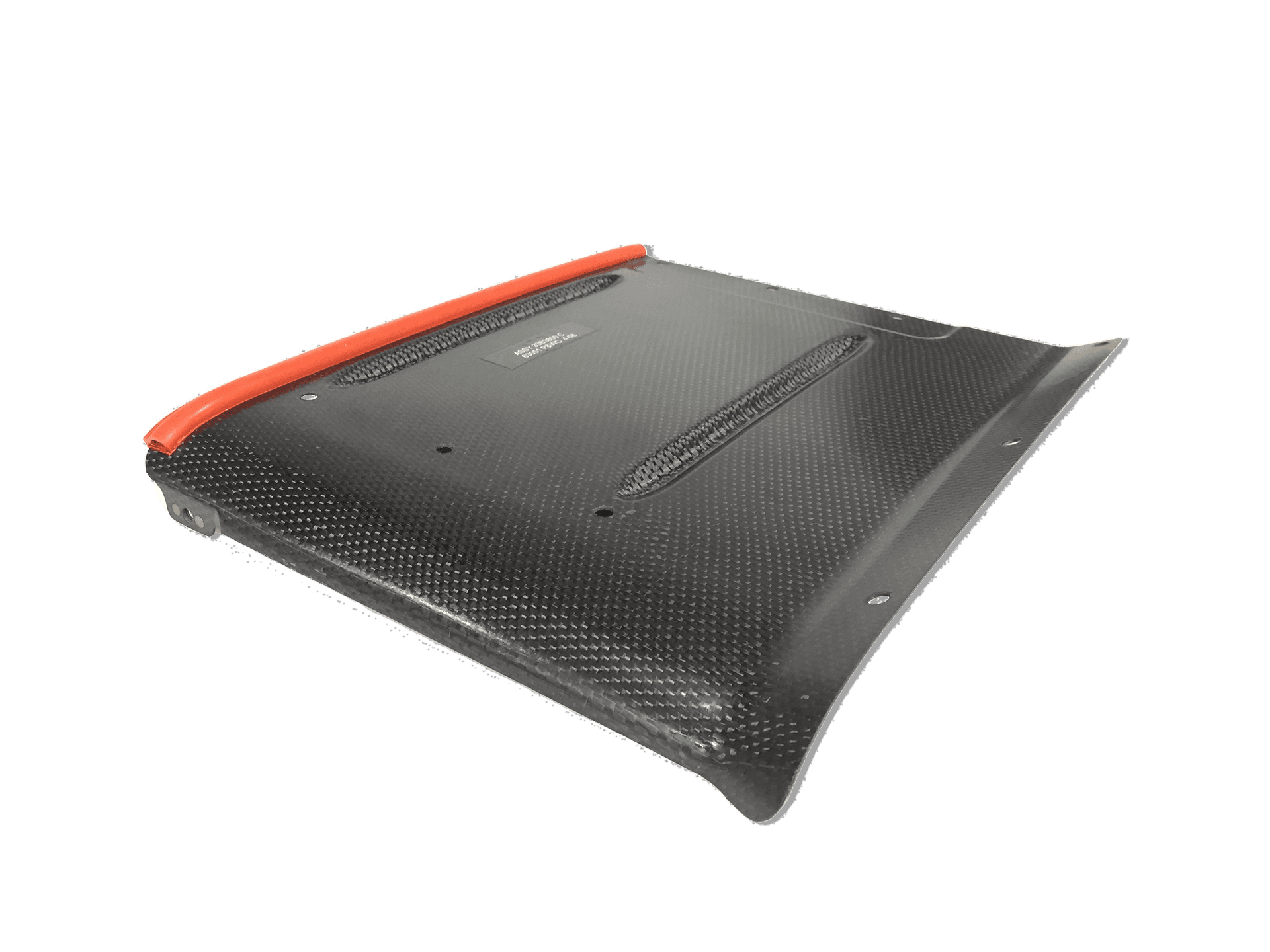
Liquid Composite Molding (commonly referred to as Resin Infusion or Resin Transfer Molding) uses thermoset resins and continuous fabric reinforcements to produce fiber-reinforced composite parts. The fabric reinforcement is applied to the mold and, if closed-tooling is used, the mold is closed. Resin, which is stored separately, is then injected into the fabric through ports that are carefully located to ensure the resin impregnates the fabric thoroughly and evenly. Polymerization occurs with the aid of heat. Following the cure cycle the part is demolded and sent along to finishing processes such as trim and drill.
Our suite of resin infusion technologies:
- Focuses on low cost, high quality processes
- Maximizes use of analysis to eliminate the number of iterations to achieve an acceptable part
- Flow modeling software for tool design
- Simulation of layup
- Programming of CNC equipment
- Cure kinetics modelling for cure optimization
- Is adaptable to a wide range of aerospace applications
We employ two resin infusion methods to achieve high performing, lightweight parts:
- Resin Transfer Molding (RTM)
- Vacuum Assisted Resin Transfer Molding (VARTM)
Resin Transfer Molding (RTM)
Resin is injected under pressure into a two-sided mold. The mold and the resin can be heated, depending on application. For high temperature applications, a post cure stage is added to obtain the required material properties.
Vacuum Assisted Resin Transfer Molding (VARTM)
VARTM is a modified version of RTM where resin is pulled into the mold by vacuum rather than injected into the mold under pressure. The elimination of pressure allows for the use of lower cost composite tooling – VARTM uses one-sided molds with bagging film on the B side. The tooling is designed to be able to hold a vacuum and have a flange that is wide enough to seal the bag to the tool. Excess resin is extracted through vacuum tubing, leaving a product with less resin and lower weight.
Pressable Prepregs
Applications:
- Best suited for high rate production
Benefits:
- Net shape parts are produced by the mold requiring only de-flashing
- Sub 10-minute cycle times can be achieved
- Highly complex part geometries can be produced
- Material strength nearly matches traditional prepreg material strength
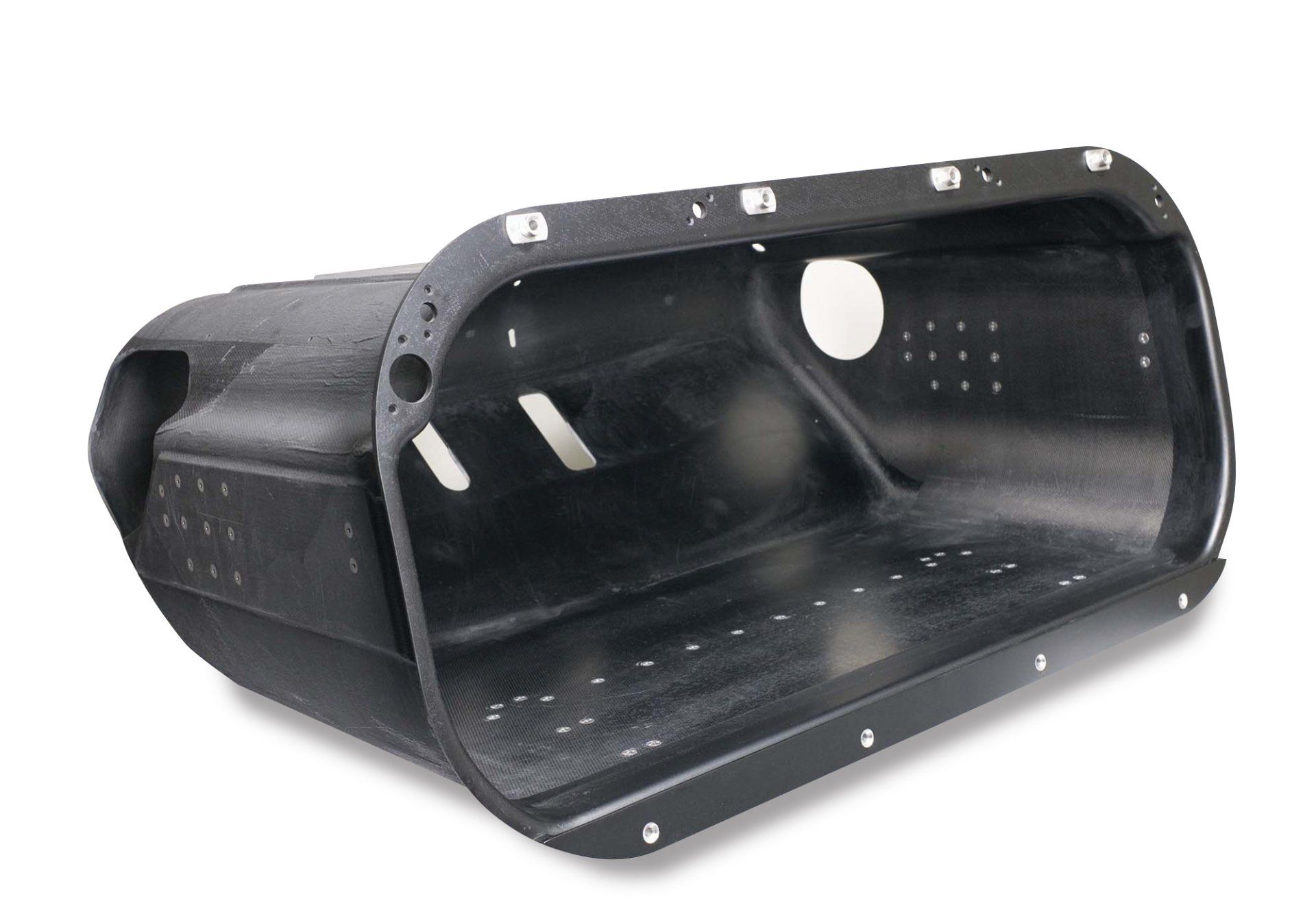
Using a specially developed prepreg, plies are cut using a CNC ply cutter and assembled into a preform. This preform is placed in a preheated mold installed in a platen press, which is closed and held under high pressure to cure the part. The part produced is net shape and requires only removal of flash. This process is well suited to higher volume parts, as this process can produce parts at a rate of one every 10 minutes. Using carbon fiber prepregs, this process produces parts that are 90% the strength of traditional prepregs but can have much more complex geometries, including complex section thickness changes over the part, and integral out-of-plane ribs and stiffeners. Due to the molding pressure required and the need for a closed mold, this process is best suited to small and medium-sized parts.
Out-of-Autoclave Prepreg Layup
Applications:
- Best suited for prototypes, large, low- to medium- volume yet complex structures
Benefits:
- Low cost compared with autoclave methods
- Pre-preg ensures optimal resin to fiber ratio
- Parts can be stiffened with a wide variety of types of core
- Multiple tooling options allow the use of low-cost tooling for prototypes, and high-durability tooling for production
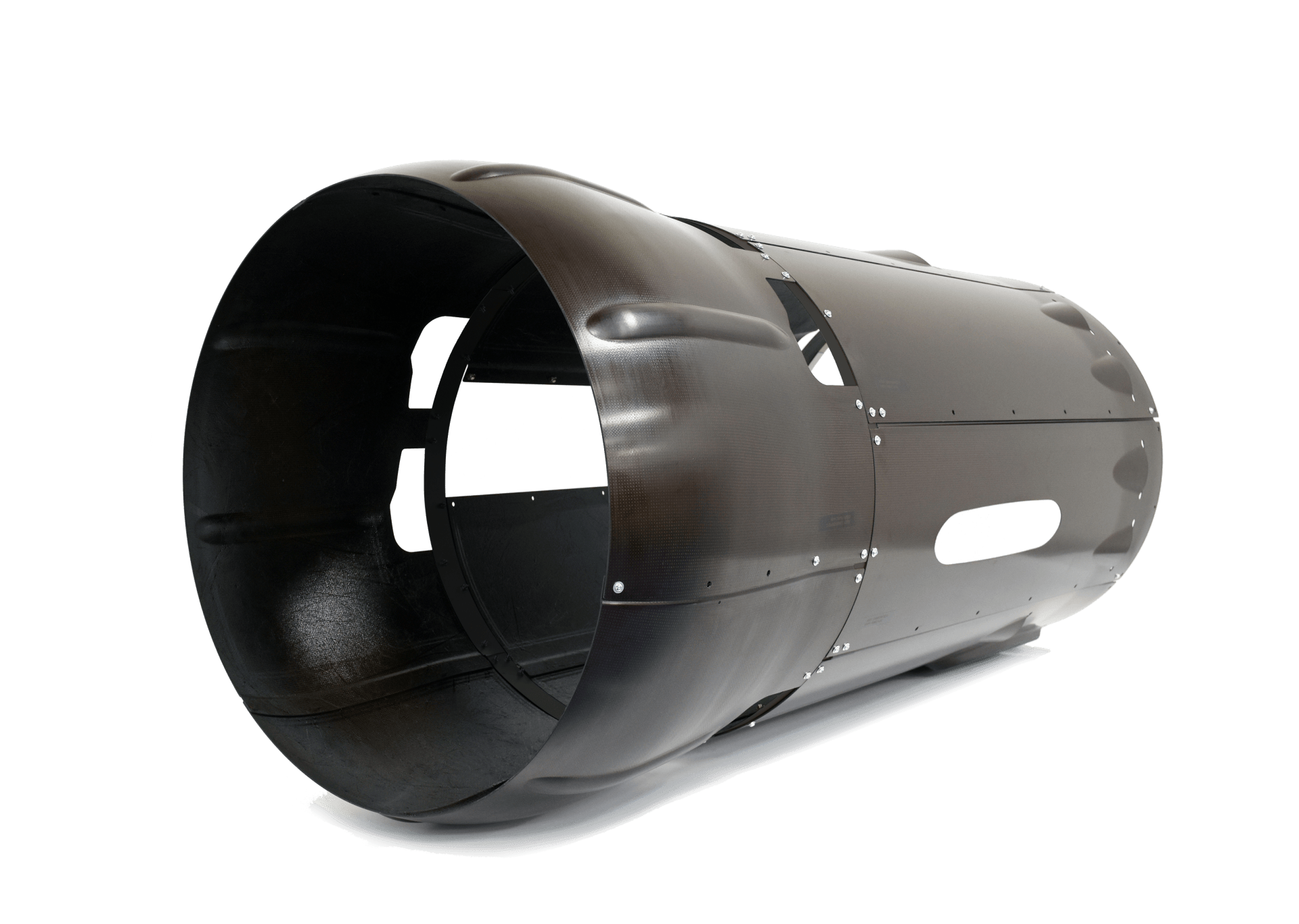
Out-of-Autoclave (OOA) Prepreg layup is best suited for large, complex and high performance parts for prototypes or for low-to-mid volumes. As inferred from the name, OOA Prepreg Layup uses prepregs (fabric pre-impregnated with resin) to layup parts which are then cured without the use of an autoclave. A range of prepreg materials can be used to meet weight, stiffness, strength and other performance goals. Typically, we use prepregs of fiberglass, Kevlar, or carbon fiber. We develop resin cure kinetics models, ensuring we select the optimum processing cycles to achieve the material properties for any given application.
Vacuum Bag Prepreg Layup
Pre-preg lay-ups in one-sided molds with bagging film on side B is a widely used technique for fabricating a vast number of complex shaped parts. We use our material know-how and software systems to orient plies, and to operate and monitor oven heat profiles to achieve the required properties. The use of ply cutting minimizes waste, shortens lay-up time and improves part-to-part consistency.
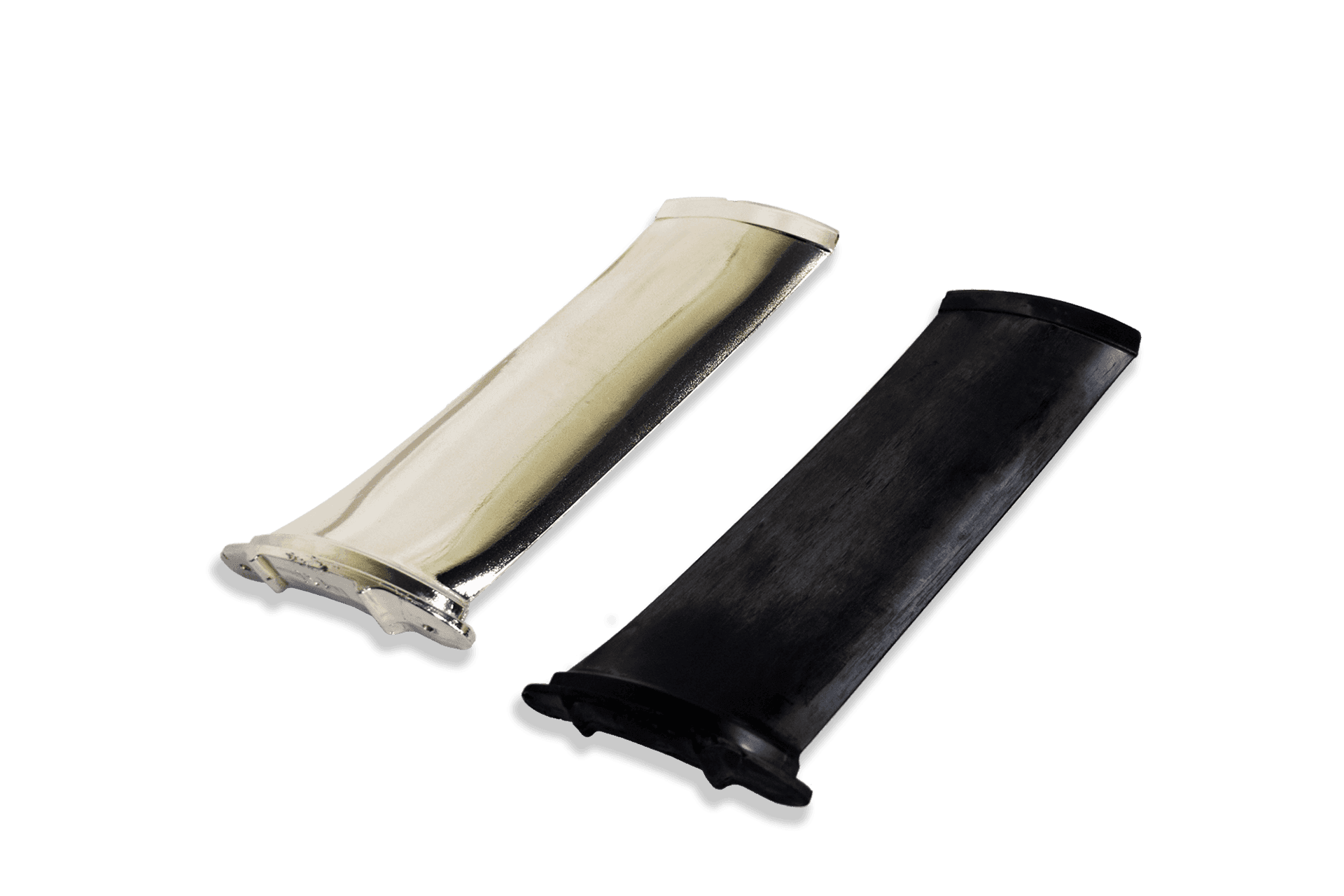
Inflatable Mandrel Prepreg Layup
For hollow shaped components like ducts, a one-sided tool with an inflatable mandrel is used to achieve the component geometry. Pre-preg is laid up over the mandrel then positioned inside the mold and the mould is closed and heated. Resin will flow under the pressure from the mandrel as it is inflated to create the final hollow shape. On airplane ducts, the use of carbon fiber pre-preg is an excellent choice for strength and light weight.